As technological advances continue to revolutionize data and network applications, it’s been clear as day that data centers and other networking infrastructures need more efficient systems to handle their increasing workload. With the introduction of fiber cables a few decades ago, there was a significant upgrade to the lines used at the time.
Base-12 cables were the industry standard for fiber optic links and were effective for many years. While some businesses still use them, others needed an upgrade to enhance the performance of their network.
As a result, Base-8 cable connectors were introduced to the market and provide a solution for anyone looking to boost their IT infrastructure. Read on to learn more bout Base-8 fiber optics and how your business can benefit from making the switch.
What are the Best Base-8 Cable Connectors?
Before discussing Base-8 cables, we’ll need to give you some brief insight into cable connectivity. As we stated above, Base-12 cables were the industry standard for most networking applications.
However, they arose from problems with Base-2 systems, which had two fibers present on a capable. These cables provided limited network connectivity for large data infrastructures.
As the name suggests, Base-12 cables are designed to hold 12 fibers simultaneously and have given organizations increased efficiency for their networking operations.
But with the advancement of technology systems, data centers need increased efficiency, leading to the birth of Base-8 fibers. These systems use increments of 8 for their fiber-optic links and come with more Ethernet capacity.
Before Base-8 cables were introduced, Ethernet capacity was limited to 10G. However, they have increased capacity from 40G to 400G, depending on your networking applications.
Related: Fiber Connector Types Buyer’s Guide [2021]
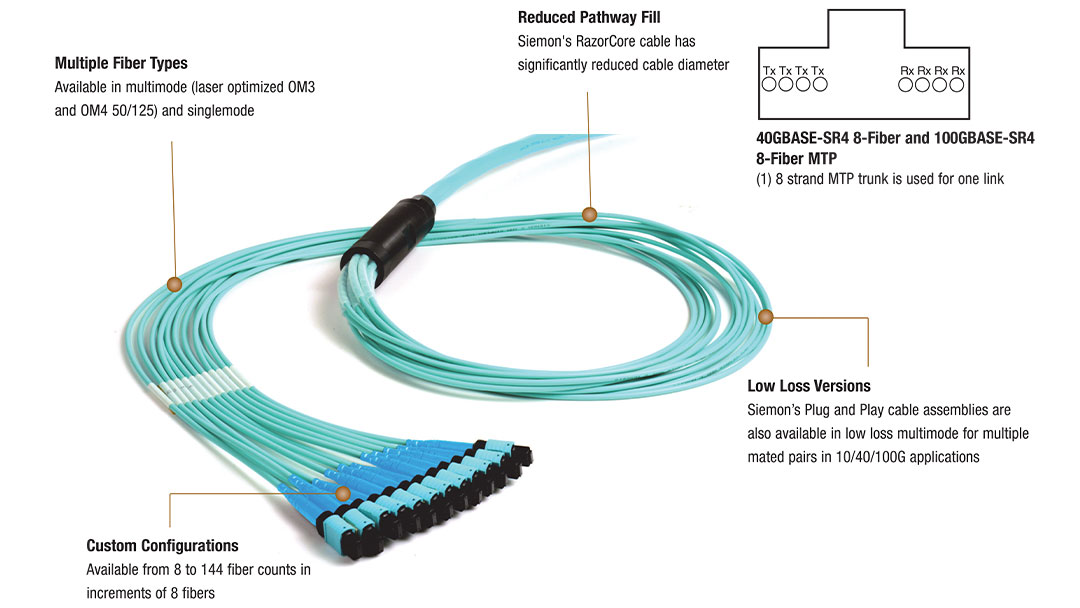
Benefits of Base-8 Cable Connectors
When looking at the differences between Base-8 and Base-12 cables, the most obvious difference is the number of fiber connectivity increments each has. You would think Base-12 solutions provide more efficient solutions since there are more connectivity options.
However, that isn’t the case. A common problem with Base-12 connectivity is unused ports. Four ports are used to transmit, and four are receiving. But that leaves four ports empty, which can be costly and result in a lack of efficiency in your networking infrastructure.
No one wants to waste unnecessary money, especially in business. So, the best way to solve this challenge is to adopt Base-8 connectivity. It results in full utilization of your system without sacrificing your fibers. But here are some other benefits of using a Base-8 fiber-optic connection:
- It can be utilized for both two and eight fiber transceiver technologies
- Provides flexibility for 40G, 100G, and 400G transmission networks
- Enables full utilization of fiber connectivity without the need for Base-12 to Base-8 converters
- Only needs unpinned MTP patch cords for any connections within the link
Although you can’t overlook the fiber per connector density, the decision depends on how quickly you migrate to 40G and 100G network speeds.
Related: What is Fiber Optics & How Does It Work
Can You Use Base-12 and Base-8 Together?
A common question we’re asked by businesses looking to enhance their network solutions is, can Base-12 and Base-8 fiber optics be used together? Well, it depends.
If you mean mixing the components of both systems and plugging a Base-8 trunk into a 12-fiber system, then the answer is “no.” They are designed with visual differences to help avoid any mix-up when connecting to the links.
A primary reason for the visual disparities is because Base-12 trunks have unpinned MTP connectors on both sides and require the use of pinned breakout modules. However, Base-8 trunks have pinned connectors on both ends.
So if you were trying to connect a Base-8 trunk into a Base-12 breakout module, it wouldn’t work. Think of it like a magnet connection. Two positives or negatives wouldn’t be able to connect to each other, and the same applies with Base-8 and Base-12 cables.
Do you want to make sure your networking equipment remains safe from human error? Check out this solution from C&C Technology Group!
Why was there this change? It is easier to increase network efficiency since Base-8 MTP patch cords have unpinned connectors on both sides. So it simplifies network solutions and eliminates the need to have multiple pinning arrangements for MTP patch cords.
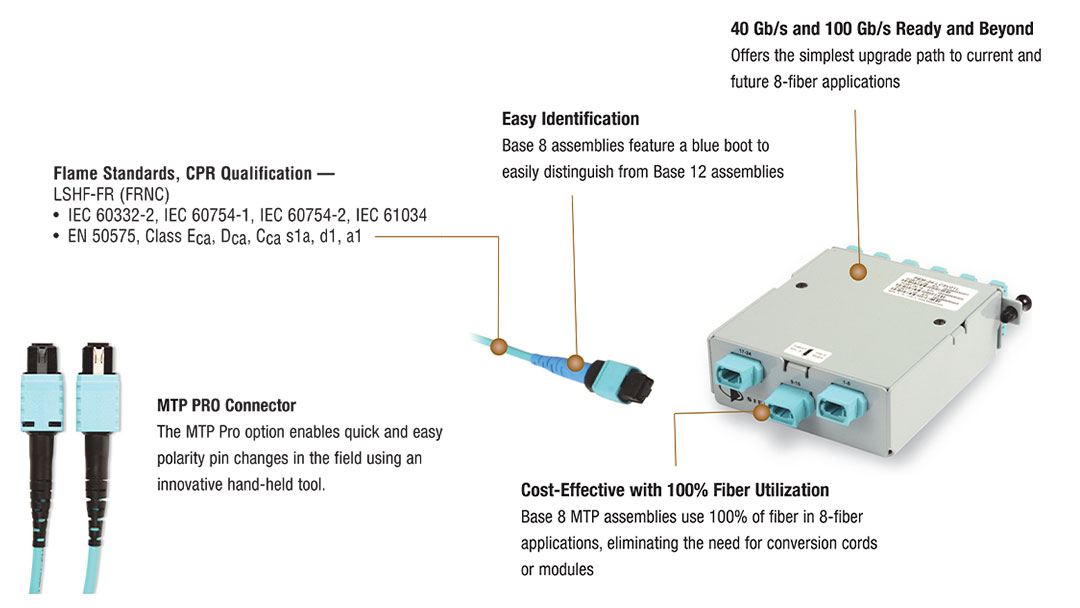
However, if by “use them together,” you mean having both a Base-8 and Base-12 connection in the same IT infrastructure, then the answer is “yes.” But there is a stipulation.
You’ll need to maintain both links independently because they aren’t interchangeable, and both Base-8 and Base-12 components can’t be plugged into each other with the same link, as stated above. So you’ll need to take great care of your physical infrastructure to ensure the links are not entangled.
Related: Fiber Splicer: Here’s Everything You Need To Know (Plus Which Is the Best One!)
We Offer the Best Base-8 Cable Connectors
Base-8 Cable Connectors and Base-12 connections will continue to be used in data centers and other networking infrastructures for a long time. While Base-12 has been the standard for many years, it does come with some limitations.
If you’re happy with a Base-12 connection and feel like it’s providing you with what your IT infrastructure needs, then there’s no need to switch. However, Base-8 Cable Connectors connectivity is an additional option that will give you a cost-effective and enhanced network solution.
Also, with its increasing popularity, you wouldn’t want to fall behind your competitors. Switch today, and increase the efficiency of all of your IT systems.
Are you looking to enhance your fiber optic network? Then contact C&C Technology Group to get started on optimizing your network today!
Last Updated on August 2, 2022 by Josh Mahan




