Data centers are critical infrastructures where IT operations are concentrated, and they house a high density of computing and storage resources. Despite the rigorous standards in place to ensure the safety and reliability of these facilities, fires are a catastrophic risk. They can lead to significant service disruption, data loss, and financial ramifications. Given the concentration of electrical equipment, along with the high power and cooling demands, data center fires are often attributed to electrical failures, overheating, and human error.
In response to the threat of fires, data center operators implement robust fire prevention and safety measures, including comprehensive disaster recovery planning, adherence to strict government and industry regulations, and continuous innovation in technological solutions. The deployment of advanced fire suppression systems and stringent operational best practices aim to reduce the likelihood of fire incidents. However, when fires do occur, understanding their causes, effects, and the measures taken to combat them is vital for improving future fire safety in data centers.
Key Takeaways
- Data center fires pose serious risks to the infrastructure and can lead to significant service disruptions.
- Extensive fire prevention and disaster recovery strategies are essential to maintain the integrity of data centers.
- Continuous advancements and adherence to regulations are crucial for enhancing fire safety in data centers.
Understanding Data Center Fires
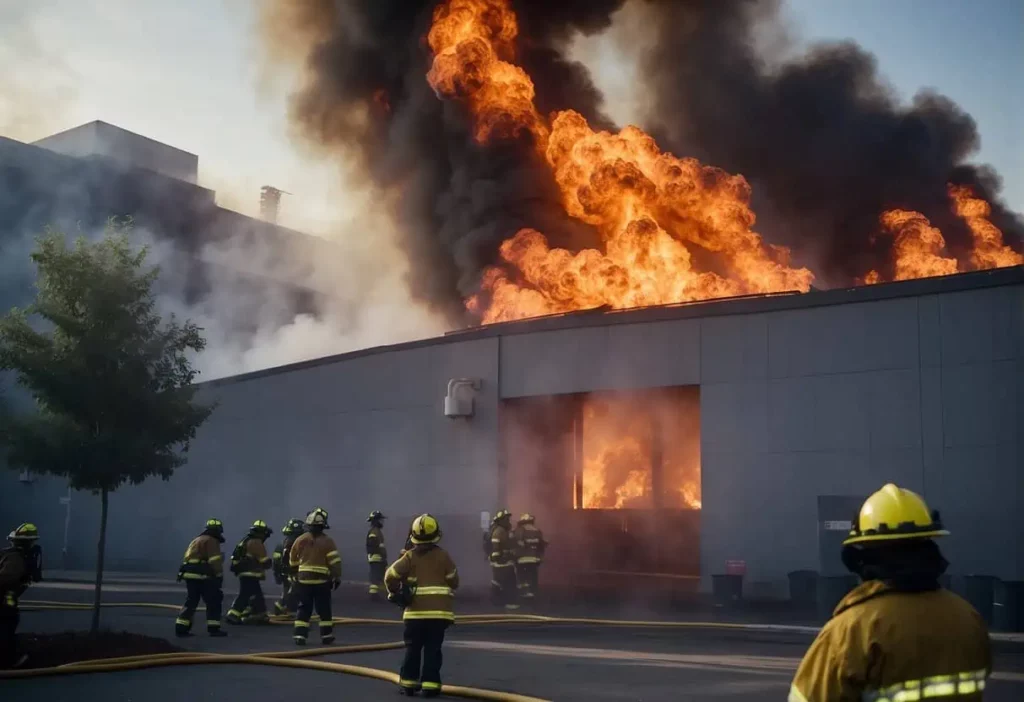

Data center fires pose a significant risk due to the dense deployment of electrical equipment and the critical nature of the IT services they support. A thorough comprehension of the causes and impacts is essential for safeguarding these sophisticated facilities.
Causes of Data Center Fires
- Electrical Failures: Faulty wiring, short circuits, and power surges are prominent factors that can ignite fires.
- Overheating Equipment: When cooling systems fail or are insufficient, the heat generated by servers and networking gear may lead to fires.
- Inadequate Maintenance: Skipping regular inspections and maintenance can allow fire hazards to go unnoticed and unaddressed.
- Human Error: Mistakes made by staff, such as improper handling of flammable materials, can inadvertently start a fire.
Impact of Fire on Data Centers
- Operational Downtime: Any fire incident, even minor ones, can lead to significant downtime, resulting in service interruptions.
- Equipment Damage: Fire and the subsequent efforts to extinguish it—often involving water or chemicals—can cause irreversible damage to sensitive IT equipment.
- Data Loss: While many data centers have backups, a fire can still lead to loss of data, particularly if disaster recovery plans are not up to date or adequately tested.
- Reputational Damage: Trust is critical for data center operators, and a fire can erode customer confidence, potentially leading to loss of business.
Fire Prevention and Safety Measures
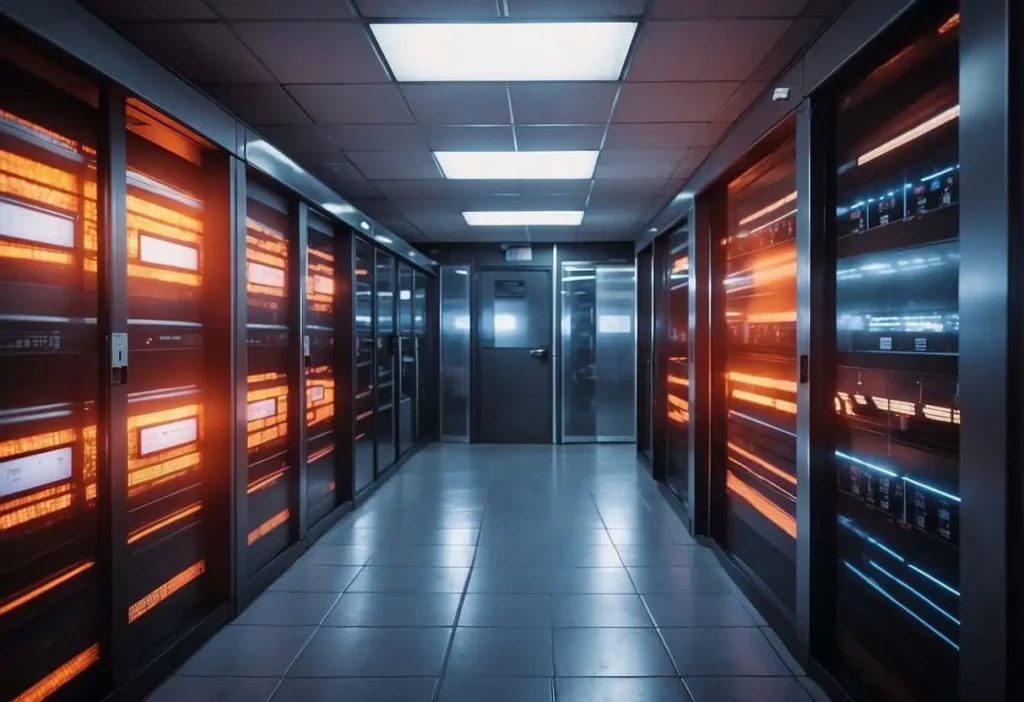

Effective fire prevention and safety measures are critical in data centers to minimize risk and ensure business continuity. These measures include comprehensive fire suppression systems, early fire detection, and regular maintenance and inspections.
Fire Suppression Systems
Data centers implement fire suppression systems to control and extinguish fires before they escalate. These systems often involve:
- Gaseous Agents: They displace oxygen or inhibit the chemical reaction of a fire. Examples include FM200 and NOVEC 1230.
- Water Sprinklers: Utilized less frequently due to potential water damage to equipment, but can be effective in certain designs.
- Pre-Action Sprinklers: These are triggered by preceding fire detection, reducing the risk of accidental discharge.
It’s vital for these systems to be designed in compliance with NFPA 75 and NFPA 76 standards for the safe operation of data centers.
Early Fire Detection
Early fire detection relies on advanced systems designed to identify the presence of fire at the earliest stage. Data centers use:
- Smoke Detectors: Installed throughout the facility, these are sensitive to smoke particles.
- Heat Detectors: Triggered by changes in temperature, indicating a potential fire.
- Flame Detectors: These sensors detect the infrared or ultraviolet radiation emitted by flames.
Prompt detection allows for quicker activation of fire suppression systems and evacuation protocols, significantly reducing potential damage.
Maintenance and Inspections
Maintenance and inspections are essential to ensuring all fire prevention and suppression equipment remains operational. A robust maintenance schedule includes:
- Regularly Testing Fire Systems: To verify functionality.
- Inspecting Physical Barriers: Such as fire-rated walls and floors, to confirm their integrity.
Data center operators must perform risk assessments periodically to adapt to new threats. These assessments inform the preventive measures and are a cornerstone of data center fire safety strategy.
Case Studies of Data Center Fires
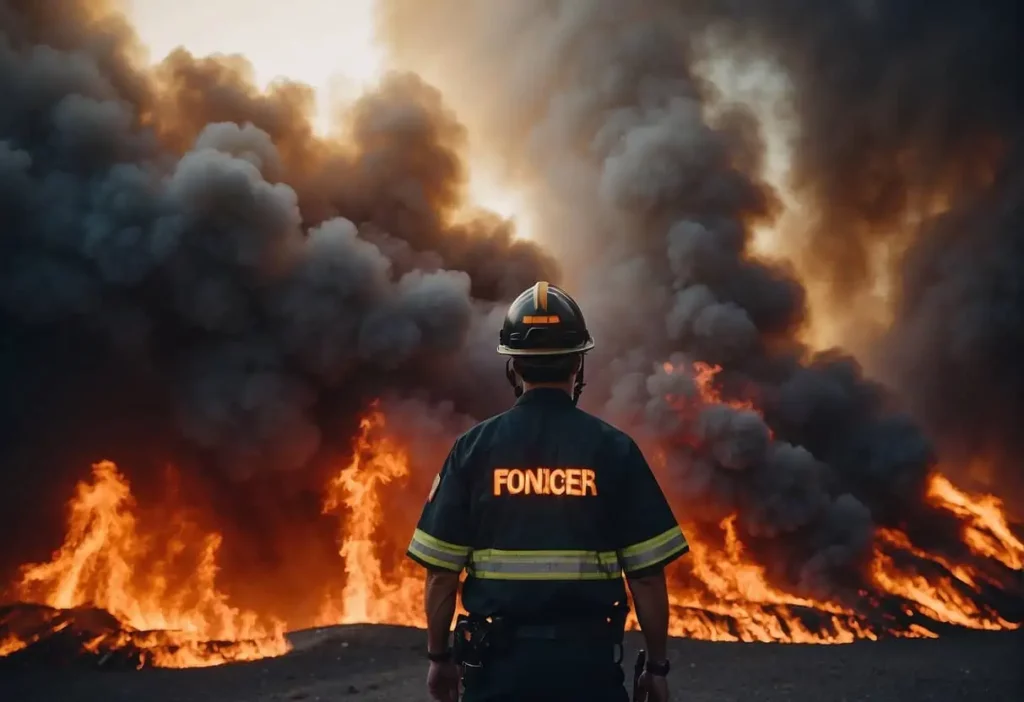

When examining the impact of fires in data center environments, case studies provide concrete examples of risks and consequences. They also highlight the importance of robust fire safety measures and the effectiveness of disaster recovery planning.
OVH Strasbourg Fire
On March 10-11, 2021, a significant fire incident occurred at the OVHcloud data center in Strasbourg, France. The fire primarily affected the SBG2 building, leading to its complete destruction; meanwhile, SBG1 also suffered considerable damage. The founder of OVH, Octave Klaba, actively communicated updates throughout the incident, offering transparency and timely information to the affected users.
- OVHcloud Strasbourg Facility:
- Impacted Buildings:
- SBG2: Completely destroyed by the fire.
- SBG1: Sustained partial damage.
- Response: OVHcloud’s disaster recovery efforts were initiated promptly, but the significant loss at SBG2 was irreversible.
- Octave Klaba’s Role: Utilized social media and public statements to provide continuous updates on the situation and recovery efforts.
- Impacted Buildings:
The Strasbourg fire serves as a reminder of the vulnerability of data centers to such disasters and underscores the critical nature of disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies.
Disaster Recovery Planning
Disaster recovery planning is crucial for data centers to ensure the protection of critical data and the continuity of business operations. A comprehensive disaster recovery plan (DRP) minimizes the impact of a fire and outlines procedures to resume functions swiftly.
Developing Disaster Recovery Plans
A disaster recovery plan is a documented, structured approach with instructions for responding to unplanned incidents. This plan includes preparations for safeguarding an organization’s data integrity, availability, and security. The initial step in developing a DRP is conducting a thorough risk assessment to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities and to quantify the impact of these risks.
Key Components of DRP Include:
- Risk Assessment: Evaluates the likelihood and consequences of fire incidents.
- Identification of Critical Assets: Pinpoints what must be protected with priority.
- Data Backup Solutions: Determines where and how to securely backup data.
- Recovery Strategies: Establishes methods for restoring data center services.
- Communication Plan: Clearly describes the roles and responsibilities for executing the recovery plan.
Business Continuity Strategies
Business continuity strategies intersect with disaster recovery, focusing on maintaining essential functions during and after a disaster. Business continuity ensures that data centers can continue to operate despite serious incidents or disasters.
Business Continuity Planning (BCP) Should Address:
- Business Impact Analysis (BIA): Identifies and evaluates the effects of business function disruptions.
- Continuity of Operations: Outlines procedures and resources necessary to keep core functions running.
- Contingency Plans: Prepares procedures for moving to alternate sites if needed.
- Regular Testing and Exercises: Ensures that the strategies are effective and staff are familiar with them.
Together, a solid disaster recovery plan and robust business continuity strategies form a shield that protects data centers from the potentially devastating impact of fires, enabling them to recover operations quickly and mitigate losses.
Government and Industry Regulations
In the realm of data center operations, adherence to government and industry regulations is crucial. These standards are designed to minimize the risk of fire incidents and to establish protocols for response and recovery, providing a framework for both legal compliance and operational safety.
Compliance with Standards
Government Regulations: Governmental bodies issue regulations that data centers must comply with to ensure safety and reliability. Among these, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 75 and 76 are critical standards that provide comprehensive guidelines on fire protection requirements for IT equipment and telecommunication facilities.
- NFPA 75: Outlines fire protection requirements for data centers, including flame-resistant materials and escape plans.
- NFPA 76: Applies to the protection of telecommunications facilities with measures on fire suppression and containment.
Industry Standards: The Uptime Institute is a prominent entity providing tier classifications for data center infrastructure and operations. Data centers strive for certification from the Uptime Institute to demonstrate compliance with robust standards that often exceed government regulations.
Legal Consequences and Lawsuits
Legal Ramifications: Data centers that fail to comply with the mandated fire safety regulations may face serious legal consequences, including fines, suspension of operations, or mandatory corrective measures. The importance of regulation adherence is underscored by the potential for such penalties.
Lawsuits:
- Class-Action Lawsuits: In the event of a fire, data centers may be subject to class-action lawsuits, especially if the incident results in data loss or service interruptions.
- Individual Lawsuits: These may be filed by stakeholders affected by the fire, such as customers or business partners, claiming damages resulting from negligent fire safety practices.
Data center owners and operators must stay informed about the evolving landscape of government and industry regulations to avoid legal pitfalls and ensure the safety of their facilities and the data they house.
Technological Solutions and Innovations
In addressing fire hazards, data centers now deploy a range of technological solutions aimed at early detection and effective suppression. These systems are critically important for minimizing the risk and impact of fires.
Advanced Smoke Detection
At the forefront of fire detection within data centers are systems such as Very Early Smoke Detection Apparatus (VESDA). VESDA works by continuously drawing air into its sensor through a piped network, detecting smoke particles at a much lower level than traditional smoke detectors. The introduction of thermal cameras adds another layer to smoke detection, offering a way to identify hot spots invisible to the naked eye, often before smoke becomes visible.
- Key Features of Advanced Smoke Detection:
- Sensitivity: Capable of detecting sub-micron smoke particles
- Coverage: Comprehensive monitoring with high-sensitivity sensors
- Speed: Alerts are raised promptly, ensuring immediate action
State-of-the-Art Suppression Equipment
Once a fire is detected, the efficacy of the suppression system is paramount. Modern data centers tend to employ clean agent systems, which release chemicals that extinguish fire without leaving residue harmful to electronic equipment. Hybrid fire extinguishing systems, marrying water and inert gas, aim to maximize efficacy while minimizing damage. For power continuity, data centers rely on Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems to maintain operations without interruption or downtime due to fire-related power issues.
- Key Aspects of Suppression Equipment:
- Efficiency: Agents such as FM200, NOVEC 1230, or inert gases act quickly.
- Safety: Non-conductive and non-corrosive agents protect sensitive equipment.
- Flexibility: Options like High Pressure Water Mist (HPWM) provide localized responses.
Operational Best Practices
Effective data center operations require meticulous planning and stringent practices. Ensuring seamless functionality and safety from fire hazards necessitates specific strategies focused on system design and staff training.
Redundancy and System Design
Redundancy is critical in data center operations to prevent service interruptions. A well-implemented redundancy strategy involves the following:
- Power Supply: Dual power sources, including on-site generators, ensure continuous operation.
- Cooling Systems: Multiple cooling units and pathways preserve optimal temperatures, preventing equipment overheating.
- Data Storage: Regularly updated backups on site and at a remote colocation facility protect against data loss.
All systems should have fail-safes that activate automatically in the event of a component failure. This is particularly important in hosting solutions, where clients rely on constant uptime.
Security Protocols and Training
A robust security framework requires a blend of physical and cybersecurity measures:
- Physical Security: Multi-layered access control systems, such as biometric scanners and security personnel, prevent unauthorized access.
- Cybersecurity: Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and consistent security updates safeguard against digital threats.
Training is equally imperative:
- Fire Safety Training: Regular drills and training sessions ensure employees are prepared to respond to fire incidents, mitigating risk and aiding in swift recovery.
- Protocol Familiarity: Employees must be well-versed in operational procedures, ensuring a competent response to any contingency.
Investing in comprehensive training programs emphasizes an organization’s commitment to security and redundancy, safeguarding its client’s assets and data effectively.
Incident Response and Firefighter Role
In the event of a fire at a data center, the prompt and methodical response of firefighters is crucial for ensuring the safety of individuals and the integrity of critical infrastructure such as SBG3 or SBG4. Effectively tackling the fire and coordinating with data center staff are pivotal aspects of the incident response.
On-Site Firefighter Actions
Firefighters must assess the situation upon arrival, understanding the specific challenges presented by data center environments such as SBG3. They employ strategies designed specifically for advanced facilities, which often house a complex array of electrical systems and backup power supplies. Initial actions include:
- Securing the perimeter: Ensuring that the area around the fire scene is cordoned off for safety and operational efficiency.
- Evaluating risks: Identifying potential hazards such as electrical risks or the presence of toxic fumes.
- Fire suppression: Utilizing appropriate fire suppression techniques that won’t further damage the sensitive data equipment.
Coordination with Data Center Staff
Collaboration between firefighters and data center personnel is key to a successful response. Data center staff possess detailed knowledge of the facilities like SBG4, which can aid in the firefighting efforts. Elements of this cooperation involve:
- Sharing of site plans: Providing detailed floor plans to pinpoint critical areas and access points.
- Communicating system knowledge: Informing firefighters about the intricacies of the data center’s fire suppression and electrical systems.
- Post-incident evaluation: Staff and firefighters debrief to review the response efficacy and identify areas for improvement.
Financial and Legal Consequences
Data centers are the backbone of modern businesses, with outages resulting in severe financial losses and complex legal challenges. When these facilities face incidents such as fire, the ramifications extend beyond immediate damage, affecting profits, data integrity, and legal accountability.
Insurance and Compensation
In the event of a data center fire, businesses must navigate the intricacies of their insurance policies to assess coverage for the physical and operational damages incurred. Insurance claims can be substantial, with past incidents at companies like Sears involving lost profits amounting to millions of dollars due to center outages. Compensations are often governed by the specifics of the insurance policy, contingent upon factors such as:
- Defining events: What circumstances are covered?
- Quantifying interruption: How are lost profits calculated?
Data Loss and Responsibility
A data center fire not only poses risks to infrastructure but also to the integrity of vital data. The responsibility to safeguard data falls on both the data center management and the businesses that rely on these services. When data loss occurs, the repercussions are twofold:
- Operational Impact: Lost data can disrupt business continuity, affecting customer trust and long-term revenue.
- Legal Accountability: Determining who is liable for the lost data can lead to protracted legal proceedings, with factors like compliance with fire safety standards and negligence playing crucial roles.
The loss of data and subsequent litigation often entail extensive time and financial resources to resolve, making it imperative for companies to have robust data protection and recovery strategies in place.
Real-world Examples of Fire Responses
In analyzing data center fire incidents, particular cases provide insight into the effectiveness of response protocols and the impact on services.
South Korea’s Data Center Incidents
Kakao and Naver, two of South Korea’s tech giants, experienced significant fire incidents in their data centers located in Pangyo, just south of Seoul. On October 15, 2022, a fire broke out at the SK C&C building which hosted these data centers. The response was quick and localized, preventing the fire from spreading widely and averting a major disaster. Despite these efforts, these incidents resulted in service disruptions affecting millions of users.
- Affected services:
- KakaoTalk
- Naver Cloud
- Multiple web services
- Response:
- Immediate isolation of affected equipment
- Activation of disaster recovery plans
Global Outages and Responses
Major global players like AWS, Google, and Microsoft have faced data center outages due to various reasons, including fires. They maintain robust fire detection and suppression systems, which are critical in minimizing service disruptions.
- Notable incidents:
- AWS’s power outage in June 2021
- Google Cloud’s disruption in November 2019
- Microsoft Azure’s multiple service interruptions
- Preventative measures:
- Regular risk assessments
- Fire safety drills
- Up-to-date disaster recovery planning (DRP)
Each of these companies has a track record of responding with speed and coordination, showcasing the resilience of their infrastructures and the strength of their emergency response strategies. Disruptions, when they occur, are usually contained and resolved with minimal downtime.
Implications for Small Businesses and Service Providers
In the event of data center fires, small businesses and service providers face significant challenges with wide-ranging consequences. These entities must prioritize robust fire prevention and response strategies to ensure business continuity and safeguard client trust.
Service Interruptions and Client Impact
Small businesses and service providers often rely on cloud services to operate efficiently and serve their customers. A data center fire can lead to prolonged service interruptions, resulting in immediate business disruptions. For small businesses, a data center fire can mean an inability to access critical data, leading to operational paralysis.
- Data Loss: Essential records and customer information are at risk.
- Client Trust: Reputational damage may lead to client retention issues.
Improving Service Provider Practices
Business Continuity To mitigate the impact of data center fires, service providers must establish comprehensive disaster recovery plans that include:
- Early Fire Detection: Deploying state-of-the-art fire detection systems.
- Fire Prevention Measures: Implementing strict environmental controls and regular inspections.
By enhancing fire response protocols and educating staff, service providers can improve resilience and limit the impact on both their operations and their small business clients.
The Future of Fire Safety in Data Centers
As data centers continue to evolve, so does the approach to fire safety, with emerging trends and new technologies paving the way for enhanced prevention and suppression capabilities.
Emerging Trends in Fire Prevention
The industry is witnessing a shift towards advanced detection systems that can pinpoint the source of heat before a fire even starts. EENews Europe reports that the implementation of such systems is becoming more prevalent, enabling a proactive stance on fire safety. Moreover, data centers are adopting stricter electrical standards to mitigate the risk of fires related to lithium-ion batteries, known for their energy efficiency but also for their potential fire hazard due to thermal runaway.
Investment in Safety Technologies
Data centers are investing heavily in state-of-the-art fire suppression technologies. Clean agents like FM-200 and Novec 1230, identified in recent designs, are becoming the norm in new facilities. SK Group, with its commitment to sustainability, is an example of a firm that might consider such investments to ensure their data centers are not just effective but also safe. Safety technology investments also extend to the needs of various providers, from hosting providers to cryptocurrency exchanges such as Deribit, all of whom require robust fire suppression to protect their critical operations and client assets.
Frequently Asked Questions
Protecting a data center against fire hazards is critical due to the potential risk of significant operational and financial losses. The following subsections answer pertinent questions on fire prevention, causes, suppression, standards, incidence rates, and lessons learned from past incidents.
How can I protect my data center against fire incidents?
Data centers can be protected by implementing a comprehensive fire protection strategy that includes early detection systems, regular risk assessments, and adherence to fire code standards such as NFPA 75 and 76. Fire suppression systems should be chosen based on the specific needs and layout of the facility.
What are common causes of fires in data centers?
Common causes of fires in data centers often involve electrical failures, short circuits, and overheating of equipment. Proper air conditioning, regular maintenance, and careful management of electrical infrastructure can mitigate these risks.
Which fire suppression systems are typically used in data centers?
Data centers typically use fire suppression systems that are tailored to protect sensitive equipment without causing collateral damage. These include clean agent systems that release gases like FM200 or NOVEC 1230, and pre-action sprinkler systems that activate in response to detected heat.
What fire code standards apply to data centers?
The fire code standards that apply to data centers include NFPA 75, the Standard for the Fire Protection of Information Technology Equipment, and NFPA 76, the Standard for the Fire Protection of Telecommunications Facilities. These standards provide guidelines for construction, protection, and detection requirements.
How frequently do fire incidents occur in data centers?
Fire incidents in data centers are not common, but they do occur. The rarity of such events is attributable to the stringent prevention and protection measures in place. However, the exact frequency can vary depending on a range of factors, including facility age, maintenance, and adherence to safety protocols.
What measures were taken following major data center fires, such as the OVHcloud incident?
Following major data center fires like the OVHcloud incident, measures taken typically involve a thorough investigation to identify the cause and implementation of improved safety and disaster recovery protocols. Additionally, the incident often accelerates industry-wide reviews of fire safety standards and best practices.
Last Updated on February 12, 2024 by Josh Mahan


![Best data center racks Best data center racks [buyer’s guide]](https://cc-techgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/best-data-center-racks-1024x576.jpg)